Comprehensive Guide to Electrical Equipment Testing: Tools, Techniques, and Best Practices
Introduction to Electrical Equipment Testing
Electrical equipment testing plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, reliability, and efficiency of electrical systems across various industries. It involves evaluating the functionality and integrity of equipment and components to verify that they meet safety and performance standards. Proper testing procedures not only prevent potential hazards but also comply with legal and industry regulations. Understanding the nuances of Electrical Equipment Testing can empower businesses to maintain optimal operational practices while safeguarding personnel and assets.
What is Electrical Equipment Testing?
Electrical equipment testing refers to a systematic process of measuring the electrical parameters of various devices and systems. This includes assessing performance attributes such as voltage, current, resistance, and insulation. The goal is to identify any faults or weaknesses that might compromise the functionality or safety of the equipment. Testing can be performed on a wide range of electrical devices including transformers, circuit breakers, wiring systems, and switchboards. It may involve visual inspections, metering, and other diagnostic techniques.
Importance of Electrical Safety
Electrical safety is of paramount importance in any environment where electrical equipment is used. Ensuring the safety of personnel and the public requires thorough testing, which can prevent electrical fires, shock hazards, and equipment malfunctions. Regulatory organizations, such as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), stipulate safety standards that must be adhered to in order to mitigate risks associated with electrical systems. Engaging in regular testing also promotes a culture of safety that enhances employee morale and productivity.
Overview of Testing Standards and Regulations
Electrical equipment testing is governed by a variety of standards and regulations aimed at ensuring safety and performance. Key standards include the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), and Underwriters Laboratories (UL), among others. These standards outline specific testing protocols and criteria that must be met for equipment used in commercial and industrial applications. Compliance with these regulations is not only mandatory but also serves to enhance the credibility and marketability of products within the global marketplace.
Types of Electrical Equipment Testing
Routine vs. Non-routine Testing
Electrical equipment testing can be categorized into routine and non-routine testing. Routine testing is performed on a regular basis as part of maintenance programs. It includes practices such as inspections, visual checks, and functional tests to ensure that equipment operates as intended. Non-routine testing, on the other hand, occurs in response to specific events or anomalies, such as after a system failure or following significant modifications to the equipment. Both testing types are essential for a comprehensive safety and maintenance strategy.
Functional Testing: Ensuring Operational Integrity
Functional testing involves evaluating the operational capabilities of electrical equipment to ensure it performs its intended tasks under specified conditions. This type of testing verifies that all controls and indicators are functioning correctly and that the system responds appropriately to operational demands. Techniques may include load testing, capacitance measurements, and operational simulations. Proper documentation of functional tests is crucial for tracking performance over time and supporting compliance with regulations.
Electrical Safety Testing: Methods and Protocols
Electrical safety testing encompasses a variety of methods aimed at verifying the safety of electrical equipment. Common protocols include the insulation resistance test, earth continuity test, and high-potential (hipot) test. Insulation resistance testing checks for adequate insulation levels to prevent electrical leakage, while earth continuity testing verifies the integrity of grounding systems. The hipot test applies a high voltage to ensure the insulation can withstand the operational environment. By using these protocols, companies can effectively assess their equipment’s safety and reliability.
Tools and Instruments for Electrical Equipment Testing
Essential Testing Equipment and Their Uses
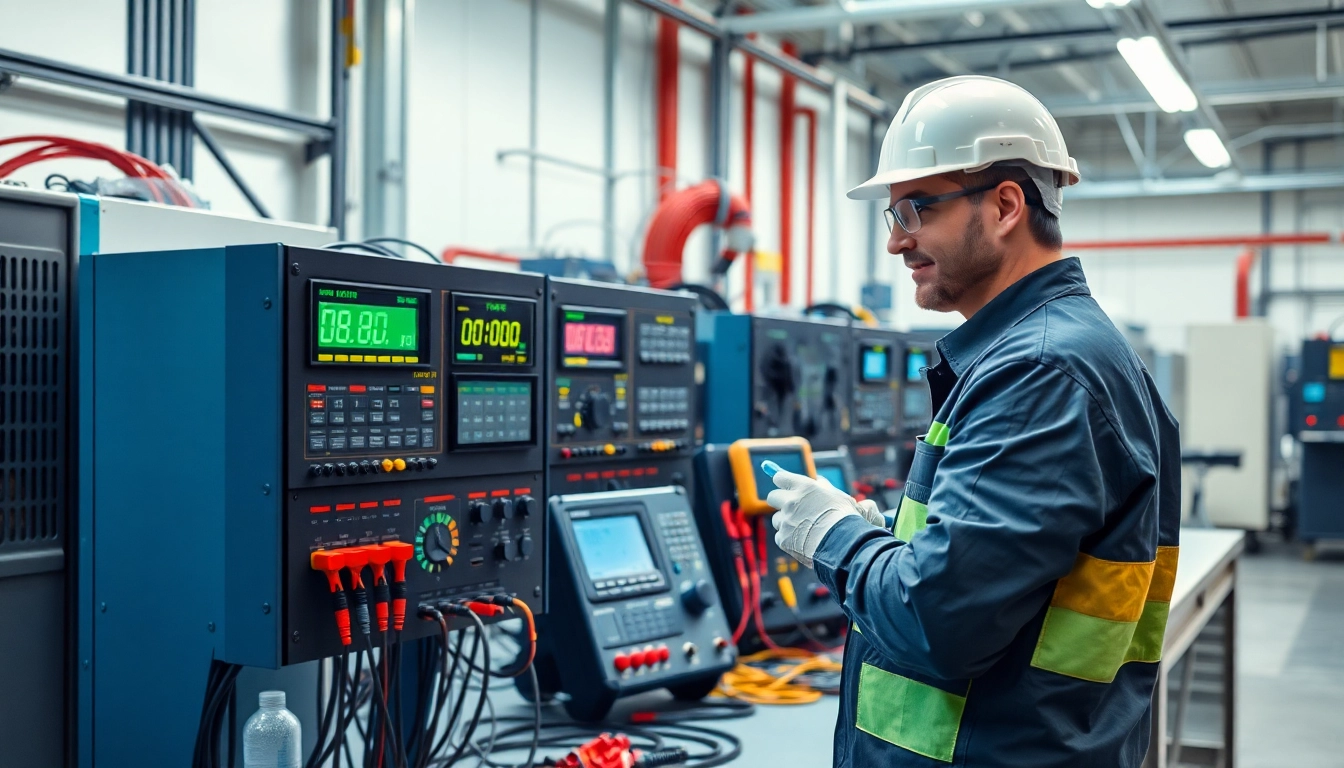
To conduct comprehensive electrical equipment testing, various tools and instruments are required. These may include multimeters, insulation testers, ground resistance testers, and power analyzers. Multimeters are versatile instruments used for measuring voltage, current, and resistance, while insulation testers specifically evaluate insulation integrity. Ground resistance testers are essential for ensuring the effectiveness of grounding systems, and power analyzers provide in-depth analysis of power quality and consumption. Each tool serves a specific function, and selecting the right equipment is pivotal for accurate testing outcomes.
Advanced Technologies in Electrical Testing
Advances in technology have significantly enhanced electrical equipment testing capabilities. Digital multimeters, which provide greater accuracy and additional features such as data logging and analysis, have largely replaced traditional analog models. Furthermore, automated testing systems streamline testing processes, improve efficiency, and minimize human error. Infrared thermography is another advanced technique used for identifying electrical hotspots and potential failures before they escalate. The integration of sophisticated software solutions aids in data management and trend analysis, making it easier for businesses to monitor equipment health over time.
Best Calibration Practices for Accurate Results
Calibration is imperative to maintain the accuracy of testing equipment. Regular calibration ensures that measuring instruments provide reliable results, which is essential for compliance with industry standards. Calibration procedures should be documented and followed rigorously, utilizing standards such as ASTM or ISO guidelines. Implementation of a calibration schedule can help in tracking the performance of devices, and using certified calibration services is crucial for unbiased results. Proper calibration contributes to the integrity of the testing process and promotes trustworthiness in the findings.
Best Practices for Conducting Tests
Preparing for Electrical Equipment Testing
The preparation phase for electrical equipment testing is critical in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the results. This involves establishing a clear testing plan that outlines objectives, methodologies, and metrics for success. Personnel should receive appropriate training to understand the testing procedures and equipment involved. Additionally, ensuring that all necessary tools and documentation are available before beginning the tests can help reduce delays and errors. A thorough risk assessment should be conducted to identify potential hazards and implement necessary precautions.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Electrical equipment testing environments may present various challenges, including unforeseen equipment failures, personnel safety concerns, and regulatory compliance issues. To overcome these obstacles, effective communication and planning are vital. Implementing a robust maintenance program can mitigate the risks of unexpected failures, while fostering a safety culture ensures employees feel comfortable addressing potential hazards. Regular reviews of regulatory guidelines and training can provide assurance that compliance standards are met. By anticipating challenges and developing strategies to address them, testing processes can be executed smoothly.
Documenting Test Results Effectively
Accurate documentation of test results is essential for tracking equipment performance and ensuring compliance. Results should be recorded systematically, utilizing standardized forms or software solutions that facilitate easy data retrieval and analysis. Each test record should include details such as date, type of test conducted, equipment involved, environmental conditions, and results obtained. Conducting audits of documentation processes can help identify areas for improvement and ensure that records are comprehensive and accessible for future reference.
Future Trends in Electrical Equipment Testing
Integrating IoT in Electrical Testing
The Internet of Things (IoT) is profoundly transforming electrical equipment testing practices. By integrating IoT devices, companies can monitor equipment health in real time, collecting data that can be used to predict potential failures and optimize maintenance schedules. Sensors placed on equipment can continuously assess performance metrics, alerting personnel of abnormalities before they lead to significant issues. This shift toward predictive maintenance not only enhances safety but also reduces operational downtime and associated costs.
Advancements in Testing Technology
As technology continues to evolve, the landscape of electrical equipment testing is expected to see significant innovations. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning are being deployed to enhance data analysis and improve predictive capabilities. These technologies can identify patterns in testing data that may not be immediately recognizable to human analysts, allowing for more proactive maintenance efforts. The integration of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) for training and simulation purposes also signifies a shift toward more immersive and effective learning environments for technicians.
Impact of Regulations on Testing Practices
Regulatory requirements are continuously evolving to adapt to advancements in technology and changing safety standards. Organizations must stay informed about the latest updates to regulations affecting electrical equipment testing to ensure compliance. Increased scrutiny from regulatory bodies is likely as safety concerns grow, and businesses will need to be proactive in their testing practices. Regular training for personnel and implementing robust quality management systems will be essential in maintaining compliance and adapting to changes in testing protocols.











Post Comment